Studying the brain to build AI that processes language as people do – Meta AI
Meta AI is announcing a long-term research initiative to better understand how the human brain processes language. Meta AI will use insights from this work to guide the development of AI that processes speech and text as efficiently as people. The data sets were collected and shared by several academic institutions, including Max Planck Institute for Psycholinguistics and Princeton University, with the consent obtained from the study participants.
Introducing CommerceMM: A new approach to multimodal understanding for online shopping – Meta AI
Meta AI’s CommerceMM is a new approach to multimodal understanding for online shopping. Because so many product posts rely on both text and images, comprehension is crucial to make products more discoverable. CommerceMM relies on a novel set of pretraining tasks, called omni retrieval, to fuse the model’s characterizations of a post’s text and image, creating a representation of the post as a whole. An early version of CommerceMM has been deployed to provide more relevant search results and recommendations across Instagram Shops, Facebook.
Designing a strong test for measuring true common-sense reasoning – Nature Machine Intelligence
Common-sense reasoning has recently emerged as an important test for artificial general intelligence, especially given the much-publicized successes of language representation models such as T5, BERT and GPT-3. More comprehensive evaluation methods that are grounded in theory should be developed to test the complexity of common sense reasoning, authors say. The advent of such models has led to a newfound focus on developing powerful artificial intelligence capabilities of a general nature.
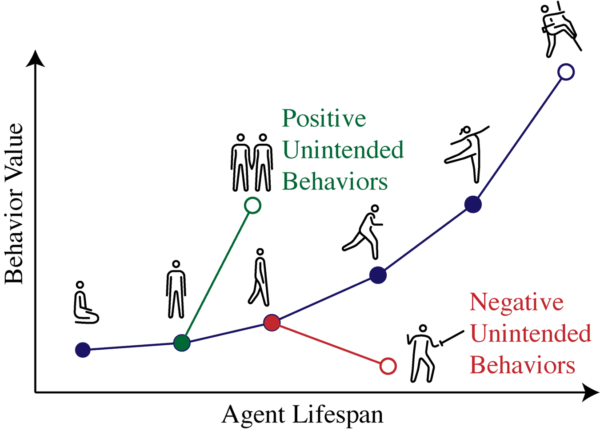
Designing Societally Beneficial Reinforcement Learning Systems – Berkeley AI Research
Deep reinforcement learning (DRL) is transitioning from a research field focused on game playing to a technology with real-world applications. Notable examples include DeepMind’s work on controlling a nuclear reactor or improving Youtube video compression. But the exciting potential for real world applications of RL should come with a healthy dose of caution. RL policies are well known to be vulnerable to exploitation, and methods for safe and robust policy development are an active area of research.
Significantly faster Vision Transformer training – Meta AI
Vision Transformers (ViTs) can achieve state-of-the-art results in visual representation and recognition. But as models begin to exceed teraflops scale, the field has come up against major bottlenecks. Training a single model can take months and require hundreds or thousands of GPUs, inflating accelerator requirements. To broaden access to ViTs, we have developed methods to make training more efficient.
A new method for asynchronous federated learning – Meta AI
We believe we are running the first asynchronous FL system at scale, training a model on 100 million Android devices. With the ability to scale to millions of devices, FL can make significant leaps in training speed and improve efficiency. Our results show that our system is five times faster than synchronous federated learning and can achieve the same result (a high-accuracy model) with eight times less communication.
Meta’s Yann LeCun on his vision for human-level AI – Tech Talks
Yann LeCun is the recipient of the 2018 Turing Award. He is betting on self-supervised learning, machine learning models that can be trained without the need for human-labeled examples. He discusses possible paths toward human-level AI, challenges that remain, and the impact of advances in AI. He says we learn most of these things without being explicitly instructed by observing and acting in the world.
Democratizing access to large-scale language models with OPT-175B – Meta AI
Meta AI has released a language model with 175 billion parameters trained on publicly available data sets. The release includes both the pretrained models and the code needed to train and use them. The model will be granted to academic researchers; those affiliated with organizations in government, civil society, and academia; along with industry research laboratories around the world. We are releasing our model under a noncommercial license to focus on research use cases.
Machine learning, harnessed to extreme computing, aids fusion energy development – MIT AI
MIT research scientists Pablo Rodriguez-Fernandez and Nathan Howard have just completed one of the most demanding calculations in fusion science. They used an optimization methodology developed for machine learning to dramatically reduce the CPU time required while maintaining the accuracy of the solution. The calculation required an extraordinary amount of computer time, over 8 million CPU-hours, but what was remarkable was not how much time was used, but how little, given the daunting computational challenge.
Estimating the informativeness of data – MIT AI
MIT researchers have developed a new way to estimate good approximations to many information quantities such as Shannon entropy by using probabilistic inference. The new method opens up new applications in medicine, scientific discovery, cognitive science, and artificial intelligence. The work appears in a paper presented at AISTATS 2022 by authors Feras Saad ‘16, MEng ’16, , , and –
Understanding the world through language – Google AI
Google has seen an incredible acceleration in the field of natural language understanding. We’re finding that many of our advanced models can understand information across languages or in non-language-based formats like images and videos. Google recently added support for 24 new languages in Google Translate, spoken by over 300 million people worldwide. We’re also investing in building models that are capable of carrying more natural, sensible and specific conversations.
Combinatorial optimization with physics-inspired graph neural networks – Nature Machine Intelligence
Combinatorial optimization problems are pervasive across science and industry. Modern deep learning tools are poised to solve these problems at unprecedented scales. Here we demonstrate how graph neural networks can be used to solve combinatorial optimization problems. We find that the graph neural network optimizer performs on par or outperforms existing solvers, with the ability to scale beyond the state of the art to problems with millions of variables.
Unpacking black-box models – MIT AI
Modern machine-learning models, such as neural networks, are often referred to as ‘black boxes’ because they are so complex that even the researchers who design them can’t fully understand how they make predictions. MIT researchers created a mathematical framework to formally quantify and evaluate the understandability of explanations for machine learning models. The research will be presented at the Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics.
New advances in speech recognition to power AR experiences and more – Meta AI
Meta AI is committed to advancing the state of the art in speech technology and building the technology needed to create new augmented reality and virtual reality experiences. Tomorrow’s speech recognition systems will need to be far more efficient so they can run on-device on ultralight, compact, and stylish glasses. We’re excited to push the cutting edge further and enable people to interact with their devices.
Improving unsupervised sentence-pair comparison – Amazon Science
Many tasks in natural-language processing and information retrieval involve pairwise comparisons of sentences. The most accurate method of sentence comparison is so-called cross-encoding, which maps sentences against each other on a pair-by-pair basis. Cross-encoders, however, require annotated training data, which is labor intensive to collect. At this year’s International Conference on Learning Representations, we are presenting an unsupervised sentence-pair model we call a trans-encoder.
Setting AIs on SIGGRAPH: Top Academic Researchers Collaborate With NVIDIA to Tackle Graphics’ Greatest Challenges – NVIDIA AI
NVIDIA’s latest academic collaborations in graphics research have produced a reinforcement learning model that smoothly simulates athletic moves. These projects — and over a dozen more — will be on display at SIGGRAPH 2022, taking place Aug. 8-11 in Vancouver and online. NVIDIA researchers have 16 technical papers accepted at the conference, representing work with 14 universities including Dartmouth College, Stanford University, the Swiss Federal Institute of Technology Lausanne and Tel Aviv University.